Different Types of File Upload Types in Drupal
The File module enables you to upload and attach files to content and to manage these uploads if you accept the appropriate permissions. This module is responsible for validating file content and managing uploaded files. It also provides options for displaying file content.
Every bit a site administrator, yous volition be able to control what type of files can be uploaded and their maximum size.
The File module provides its functionality past defining a File field type for the Field module. File attachments are divers at the content blazon level (or other entities). To learn how to ascertain a field and add together it to a content type, run across Working with Field UI.
Uses
Adding a file field to a content blazon
Navigate to the "Manage fields" tab of the content type to which you wish to add the file field ( Administrate > Structure > Content types , and the link manage fields for your specific content type).
Select the field blazon file, give the field a label and machine name, click-and-drag it to the identify you want to have it among your fields, and hit the salvage button.
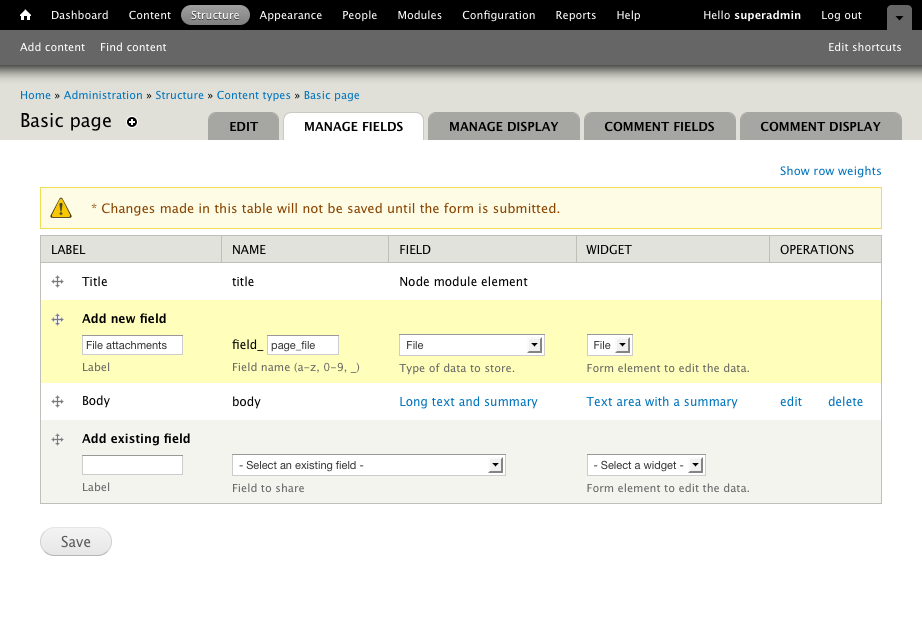
Every bit when calculation whatsoever new field, you are first required to set the field specific settings. These use for all places where you use the field. These cannot exist changed per entity.
- When checked, the Enable Display field option allows users to choose if a file should exist shown when viewing the content.
- The Files displayed by default option makes the display file selection checked by default, when users upload files to this field.
- The Upload destination past default only has the public files option bachelor – making the files bachelor right from the server (without Drupal checking any access). If y'all desire to use private files, you lot must kickoff change some settings at the file system administration page (Administer > Configuration > Media: File organization). See below for details.

The adjacent footstep is to fix the field settings for this instance only. This can exist inverse between dissimilar content types (or other entities).
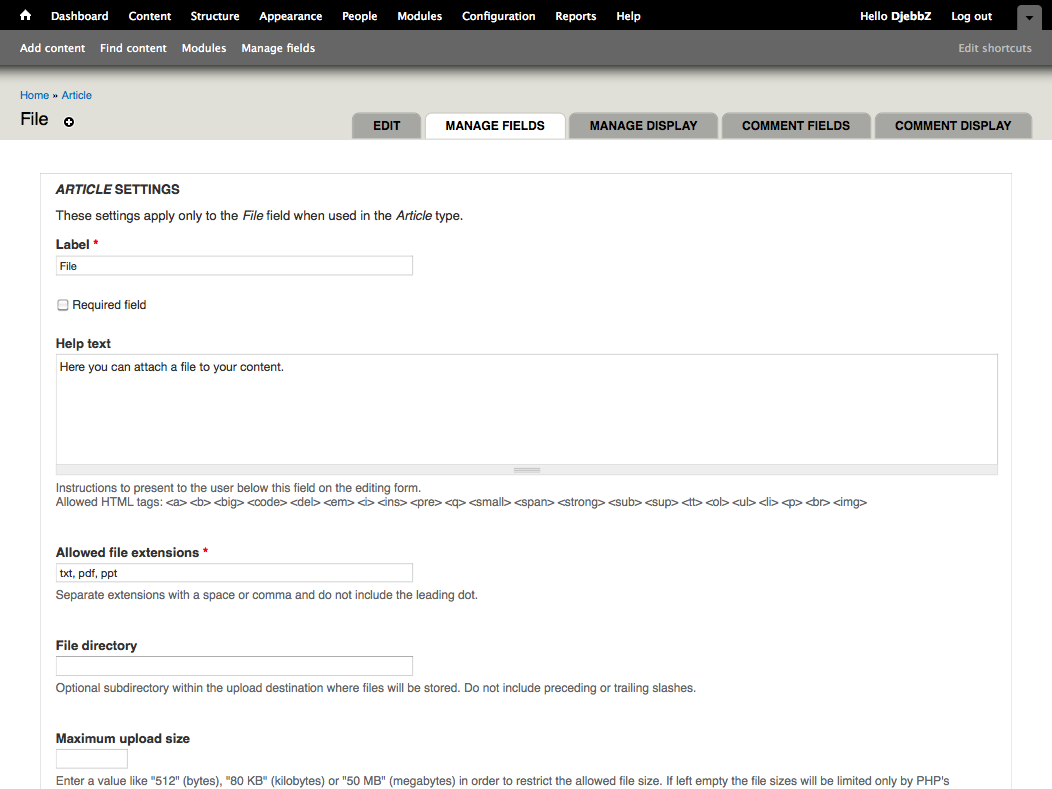
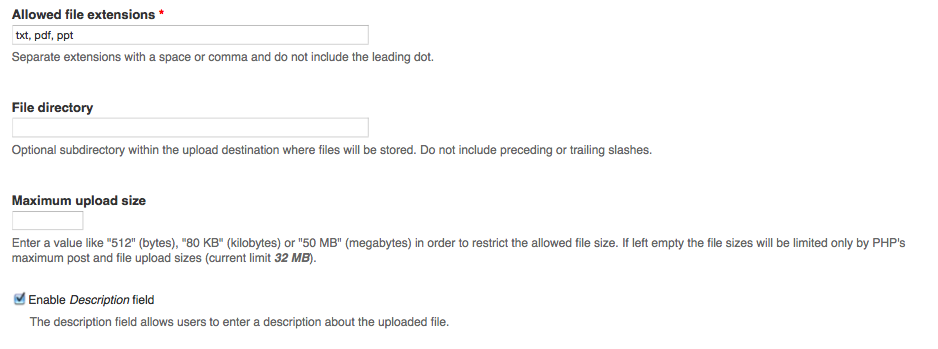
You tin add together validation options for the File field when y'all configure the content type. You must list all of the file extensions that the final user will need to be able to upload. The optional file directory where the files will be uploaded is a sub-directory of the file system path defined in the file system administration page (Administrate > Configuration > Media: File arrangement). You lot may specify a maximum file size for each file uploaded.
Managing attachment display
One time a file has been attached to content, you can specify whether information technology will exist displayed in the list of attached files or non. Listed files are displayed automatically in a department at the bottom of the content; non-listed files can for example exist embedded in your content, but are not included in the list. (Embedding a file in your content means y'all copy the path of the file and manually embed it where you desire, for example, to insert in the content equally a link tag. Note that the text format "Filtered HTML" by default refuses whatever epitome tags..)
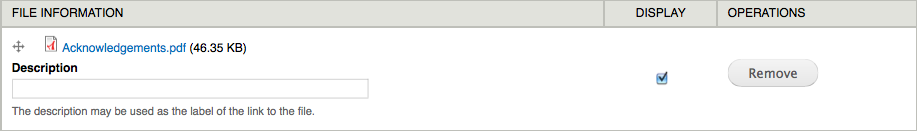
Additional options for managing the brandish of the file list are available in the "Manage brandish" tab of the specific content type's administration page (Administer > Construction > Content types and the link field display for your content type).
Managing file locations and access
When you create a file field, y'all can specify the sub-directory of the site's file organisation where uploaded files for this content type volition be stored. The site'due south file organisation paths are defined on the File system page (Administer > Configuration > Media: File system).
You can also specify whether files are stored in a public directory or in a private file storage area. Files in the public directory can be accessed directly through the web server; when public files are listed, direct links to the files are used and anyone who knows a file's URL can download the file. Files in the private directory are not accessible directly through the web server; when private files are listed, the links are Drupal path requests (for example, "/system/files/proper name-of-the-file.pdf"; here, "system/files/" is not an actual binder in the filesystem whose contents are served by the web server, but instead is a virtual URL managed past Drupal through which the individual files can be downloaded). This adds to server load and download time, since Drupal must resolve the path for each file download request, merely allows for access restrictions to be added.
The best exercise for public files is to store them in the multi-site directory like:
sites/default/files The default way to securely add a individual directory for your files is to employ a directory that tin can not be accessed straight past your web server, but can be accessed past Drupal. Ideally this directory should be located outside of your Drupal root folder.
The simple way to add a individual directory for your files is to create a sub-directory nether the public directory like:
sites/default/files/private When y'all specify the private directory in admin/config/media/file-system it will automatically create the sub-directory & create a elementary .htaccess file with Deny from all. This stops Apache from serving files from this directory. Make sure that you test this by calculation a file to that directory and verifying that you tin can't browse there directly. If this isn't working, all files in this directory will be accessible to anyone who tin gauge the URL! Notation that non-Apache web servers may need additional configuration to secure private file directories.
Whenever possible it'south recommended that you lot choose a directory located outside of your Drupal root folder (or really outside your web root), which may be tricky if you are on a shared host. If you do accept access though, you can choose a private directory which will be on the same level as your web root directory (often called public_html or www or similar) using:
../private Accessing Private Files
It is important to understand that just considering a file field is configured to apply the private file system, that does non mean Drupal volition prevent anyone from viewing files uploaded via that field. The files will be served by Drupal (via a URL like "/organisation/files/name-of-the-file.pdf"), simply Drupal will only block users' access to download the file via that URL if in that location is a specific reason to practise so.
For example: y'all accept created a new content type with a file field which stores files in your site's private file directory. Next yous create a node from this new content type and attach two new files. When the node is published links to both fastened files are visible and anyone who can view the node may download the files. Now, if you unpublish the node so that your site's end users can no longer admission it, all attached files become inaccessible for download by those users too, fifty-fifty if they apply the direct link to the files that worked when the node was published.
For effectively grained command of who can see/download fastened files you lot will demand an boosted access control module. You may write a module yourself, or use a contributed module such equally Content Access.
Private file system settings in Drupal 8
In Drupal 8, you tin can no longer set private file arrangement via UI. Y'all set it in your settings.php file. Search for this line in your settings.php:
# $settings['file_private_path'] = ''; add the url path to your individual directory. Information technology must be outside of your web root directory and be an absolute path, for case /var/www/html/example.org/individual with web root in/var/www/html/example.org/web or /home/username/example.org/private with web root in /dwelling house/username/case.org/web. And so information technology should expect like:
$settings['file_private_path'] = $app_root . '/../private'; Technical Details
PHP configuration
For file uploads to work, PHP must be configured properly. The following PHP configuration variables may demand to be gear up or configured, in your PHP php.ini file, .htaccess file, or settings.php files.
-
file_uploads = Onmust exist prepare to "On" -
upload_max_filesize = 24Mcan't exist larger thanpost_max_size -
max_input_time = 300pocket-sized values may cause timeouts for big file uploads -
memory_limit = 64Msmall-scale values may cause out of memory errors for large file uploads -
max_execution_time = 180pocket-size values may crusade timeouts for large file uploads -
post_max_size = 24Mlimits the size of input submitted to the website (including attached files)
Top Tip: Make sure you're editing the right php.ini file by going to YOURSITE/admin/reports/status/php. This volition display data about your current PHP setup which is being used for Drupal (in essence it'southward running phpinfo()). Now await for the 'Loaded Configuration File' section, this volition list the php.ini file you lot need to edit.
Clearing the Cache
It is recommended you articulate the enshroud after making these updates. If you don't, then Drupal is likely to mutter that the individual files area is not protected.
Farther Reference
- Securing file permissions and ownership
Source: https://www.drupal.org/docs/8/core/modules/file/overview
0 Response to "Different Types of File Upload Types in Drupal"
Post a Comment